Minimal ideal
In the branch of abstract algebra known as ring theory, a minimal right ideal of a ring R is a nonzero right ideal which contains no other nonzero right ideal. Likewise a minimal left ideal is a nonzero left ideal of R containing no other nonzero left ideals of R, and a minimal ideal of R is a nonzero ideal containing no other nonzero two-sided ideal of R. (Isaacs 2009, p.190)
Said another way, minimal right ideals are minimal elements of the poset of nonzero right ideals of R ordered by inclusion. The reader is cautioned that outside of this context, some posets of ideals may admit the zero ideal, and so zero could potentially be a minimal element in that poset. This is the case for the poset of prime ideals of a ring, which may include the zero ideal as a minimal prime ideal.
Contents |
Definition
The definition of a minimal right ideal N of a module R is equivalent to the following conditions:
- If K is a right of R with {0}⊆K⊆N, then either K={0} or K=N.
- N is a simple right R module.
Minimal right ideals are the dual notion to the idea of maximal right ideals.
Properties
Many standard facts on minimal ideals can be found in standard texts such as (Anderson & Fuller 1999), (Isaacs 1992), (Lam 2001), and (Lam 1999).
- It is a fact that in a ring with unity, maximal right ideals always exist. In contrast, there is no guarantee that minimal right, left, or two-sided ideals exist in a ring.
- The right socle of a ring
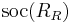 is an important structure defined in terms of the minimal right ideals of R.
is an important structure defined in terms of the minimal right ideals of R. - Rings for which every right ideal contains a minimal right ideal are exactly the rings with an essential right socle.
- Any right Artinian ring or right Kasch ring has a minimal right ideal.
- Domains which are not division rings have no minimal right ideals.
- In rings with unity, minimal right ideals are necessarily principal right ideals, because for any nonzero x in a minimal right ideal N, the set xR is a nonzero right ideal of R inside N, and so xR=N.
- Brauer's lemma: Any minimal right ideal N in a ring R satisfies N2={0} or N=eR for some idempotent element of R. (Lam 2001, p.162)
- If N1 and N2 are nonisomorphic minimal right ideals of R, then the product N1N2={0}.
- If N1 and N2 are distinct minimal ideals of a ring R, then N1N2={0}.
- A simple ring with a minimal right ideal is a semisimple ring.
- In a semiprime ring, there exists a minimal right ideal if and only if there exists a minimal left ideal. (Lam 2001, p.174)
Generalization
A nonzero submodule N of a right module M is called a minimal submodule if it contains no other nonzero submodules of M. Equivalently, N is a nonzero submodule of M which is a simple module. This can also be extended to bimodules by calling a nonzero sub-bimodule N a minimal sub-bimodule of M if N contains no other nonzero sub-bimodules.
If the module M is taken to be the right R module RR, then clearly the minimal submodules are exactly the minimal right ideals of R. Likewise, the minimal left ideals of R are precisely the minimal submodules of the left module RR. In the case of two-sided ideals, we see that the minimal ideals of R are exactly the minimal sub-bimodules of the bimodule RRR.
Just as with rings, there is no guarantee that minimal submodules exist in a module. Minimal submodules can be used to define the socle of a module.
References
- Anderson, Frank W.; Fuller, Kent R. (1992), Rings and categories of modules, Graduate Texts in Mathematics, 13 (2 ed.), New York: Springer-Verlag, pp. x+376, ISBN 0-387-97845-3, MR1245487
- Isaacs, I. Martin (2009), Algebra: a graduate course, Graduate Studies in Mathematics, 100, Providence, RI: American Mathematical Society, pp. xii+516, ISBN 978-0-8218-4799-2, MR2472787
- Lam, Tsit-Yuen (1999), Lectures on modules and rings, Graduate Texts in Mathematics No. 189, Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag, ISBN 978-0-387-98428-5, MR1653294